A toothache, a frequent dental issue, can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. The discomfort, varying in intensity, might disrupt daily routines, rest, and overall state of being. Gaining knowledge about the reasons behind tooth pain and discovering effective remedies are crucial for effectively dealing with this issue. This comprehensive guide explores the different causes of toothache and offers evidence-based solutions to relieve the pain and treat the root causes.
What Causes Toothache
1. Dental
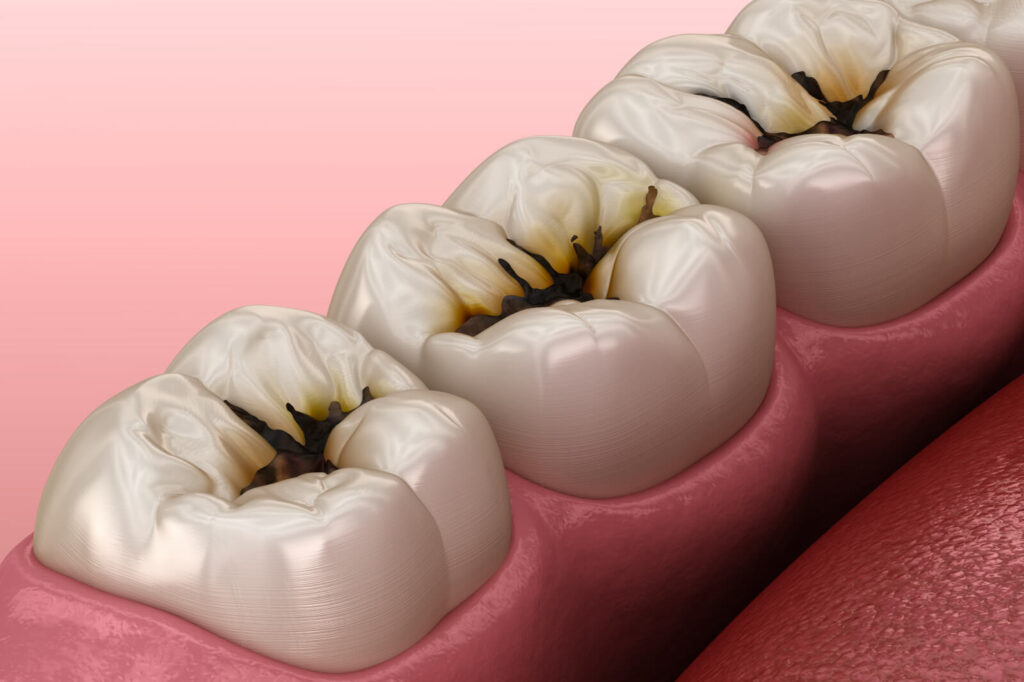
Caries (Cavities) Tooth decay, commonly referred to as cavities, is a common culprit behind tooth pain. They happen because of the erosion of tooth enamel caused by acids produced by bacteria in dental plaque. As the decay advances deeper into the tooth, it can lead to considerable discomfort.
- Symptoms: Experiencing sharp or throbbing pain, being sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli, and noticing visible pits or holes in teeth.
- Assessment: A thorough examination of your condition will be conducted, including a visual inspection and the use of dental X-rays to determine the severity of any decay.
2.Pulpitis
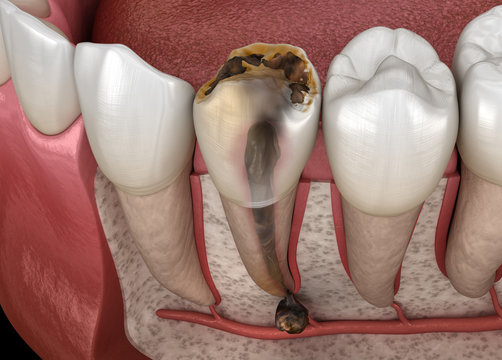
Pulpitis is a condition where the dental pulp, which is the sensitive and vital part of the tooth, becomes inflamed. The outcome can vary, either being reversible or irreversible, depending on the severity of the inflammation and damage.
- Symptoms: Experiencing intense and ongoing tooth pain, sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, and spontaneous discomfort without any apparent cause.
- Evaluation: Thorough examination, tests to determine sensitivity, and utilization of X-rays.
3.Periodontal Disease
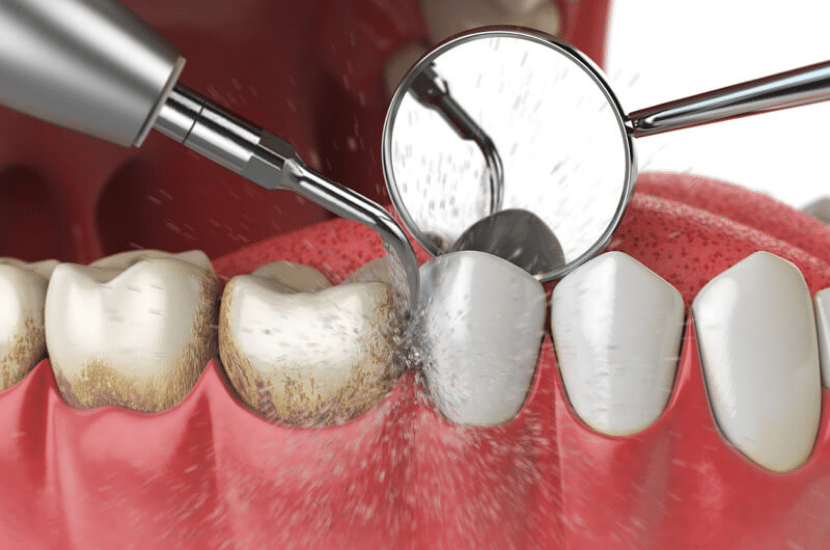
Periodontal disease, which encompasses gingivitis and periodontitis, causes inflammation and infection in the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Severe periodontal disease may result in the formation of abscesses and cause tooth pain.
- Symptoms: Swollen, bleeding gums, loose teeth, dull or throbbing pain, bad breath.
- Evaluation: Periodontal probing, dental X-rays, assessment of gum health.
4.Dental Trauma
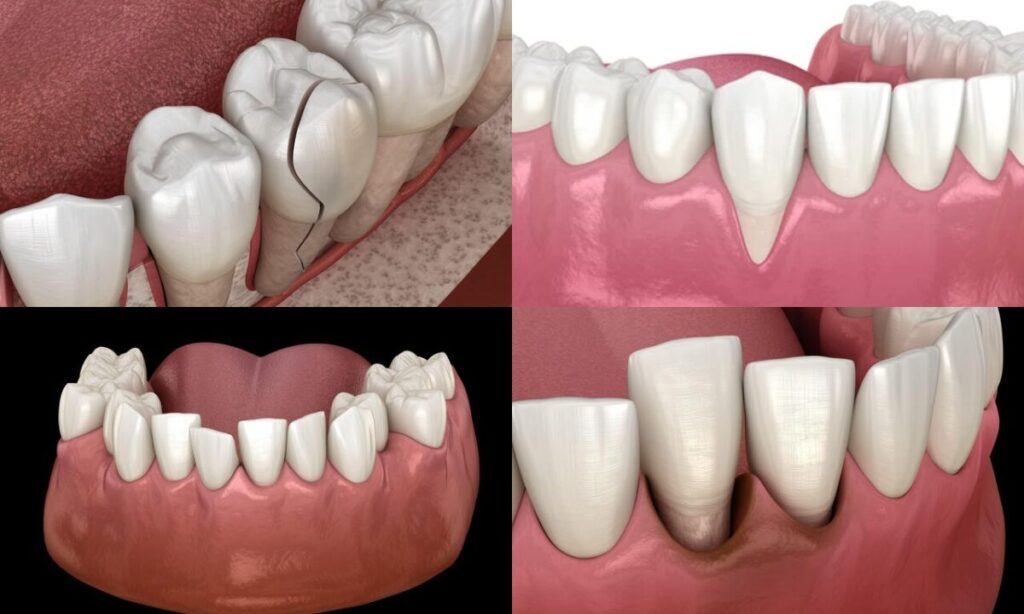
Dental Trauma Injuries to the teeth, like fractures, cracks, or dislodgement, can lead to sudden tooth pain. The pain is a result of the tooth structure being damaged and the dental pulp being exposed.
- Symptoms: Experiencing acute pain after an injury, heightened sensitivity, and noticeable damage to the tooth.
- Evaluation: Thorough examination by a medical professional, along with the use of X-rays to assess the severity of the injury.
5.Dental Abscess
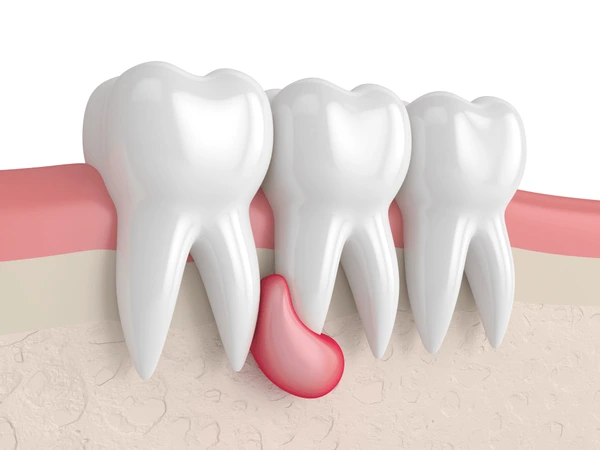
A dental abscess is a localized infection that develops a pocket filled with pus around the tooth root or gums. Typically, it arises from significant decay, periodontal disease, or an injury.
- Symptoms: Experiencing intense and ongoing pain, noticeable swelling, elevated body temperature, sensitive lymph nodes, and discharge of pus.
- Evaluation: thorough examination, imaging techniques, and tests to assess pulp vitality.
6.Tooth Eruption
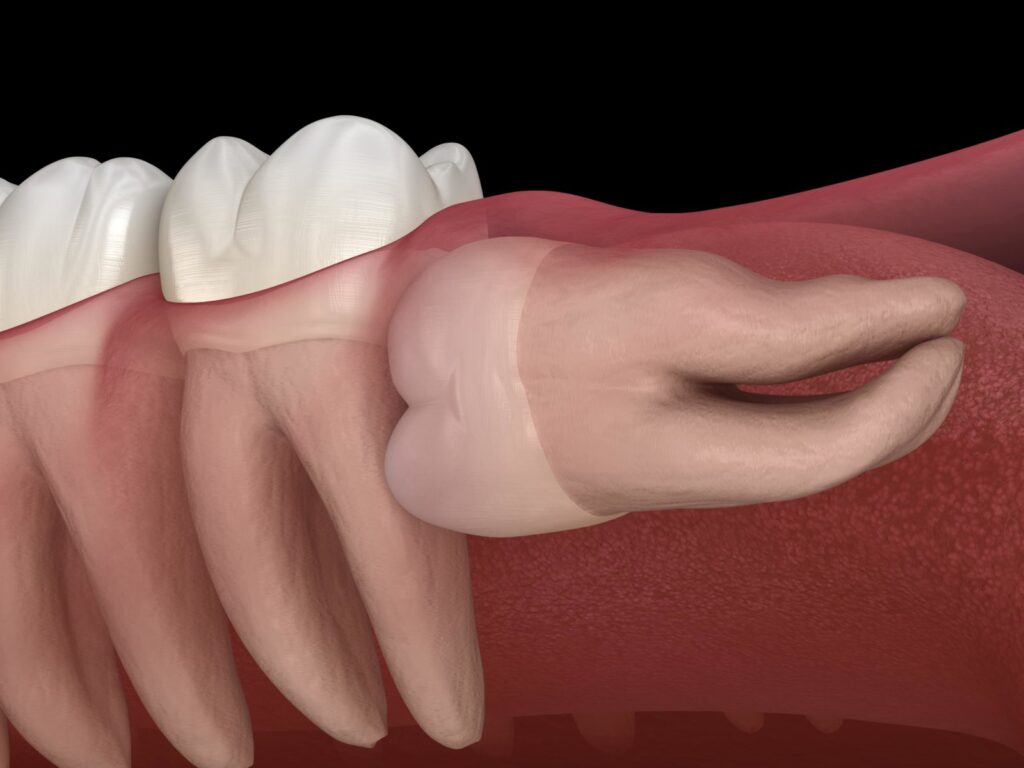
When children’s primary (baby) teeth and permanent teeth start coming in, it can sometimes lead to discomfort and toothache. Similarly, in adults, the eruption of third molars can cause discomfort and potential complications.
- Symptoms: Experiencing localized pain, swelling of gums, and difficulty chewing.
- Assessment: Examination of the area through visual inspection and palpation.
7.Bruxism Teeth
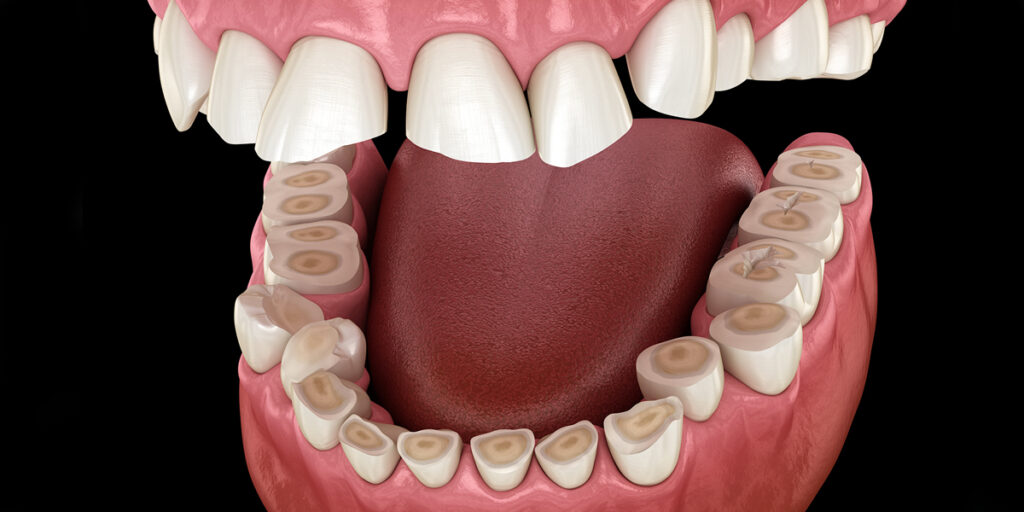
Bruxism Teeth grinding and clenching, known as bruxism, can sometimes happen during sleep and may result in toothache. Excessive forces placed on the teeth can lead to wear, fractures, and sensitivity.
- Symptoms: experiencing discomfort in the jaw, headaches, sensitivity in the teeth, and noticing wear facets on the teeth.
- Evaluation: Thorough examination and analysis of wear patterns.
8.Sinusitis
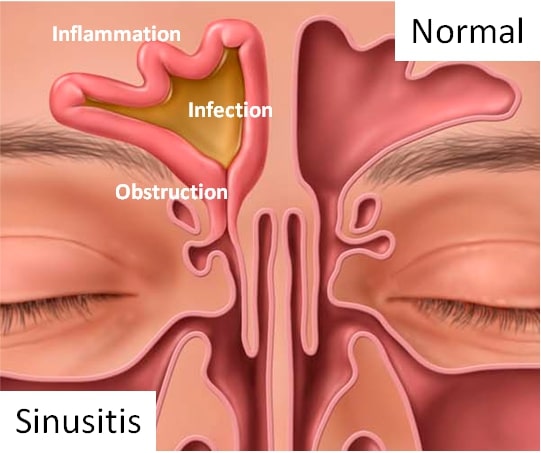
Sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinuses, can lead to discomfort in the upper teeth as they are located near the maxillary sinuses. Many people often confuse this kind of toothache with dental pain.
- Symptoms: Experiencing a dull, aching pain in the upper teeth, along with nasal congestion and facial pressure.
- Diagnosis: Clinical evaluation and the use of imaging studies such as CT scans.
9. Referred pain
Referred Pain Various conditions, including temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders and neuralgia, can lead to pain that is felt in the teeth. The pain seems to be coming from nearby structures, but it is felt in the teeth.
- Symptoms: experiencing discomfort in the teeth, along with jaw and facial pain.
- Evaluation: thorough assessment of your medical and dental background, careful examination, and utilization of imaging techniques.
Solutions for Toothache
Properly managing toothache requires addressing both the symptoms and the root cause. Here are different solutions based on the specific cause:
1. Dental caries treatment
- Restorative Procedures: Our team offers a range of options to address early-stage cavities and restore the tooth structure. We use materials like composite resin, amalgam, or glass ionomer for dental fillings.
- Root Canal Therapy: Our procedure is designed to address advanced decay that has impacted the pulp. We will carefully remove the infected pulp, thoroughly clean the canals, and effectively seal them to promote healing and restore oral health.
- Tooth Extraction: In situations where there is significant decay and the tooth is beyond repair, extraction may be required.
2.Treating Pulpitis
- Treatment for reversible pulpitis involves addressing the irritant and restoring the tooth with a filling or crown.
- Treatment for irreversible pulpitis typically involves root canal therapy or extraction. These procedures are necessary to relieve the pain and avoid any potential complications.
3. Periodontal Treatment
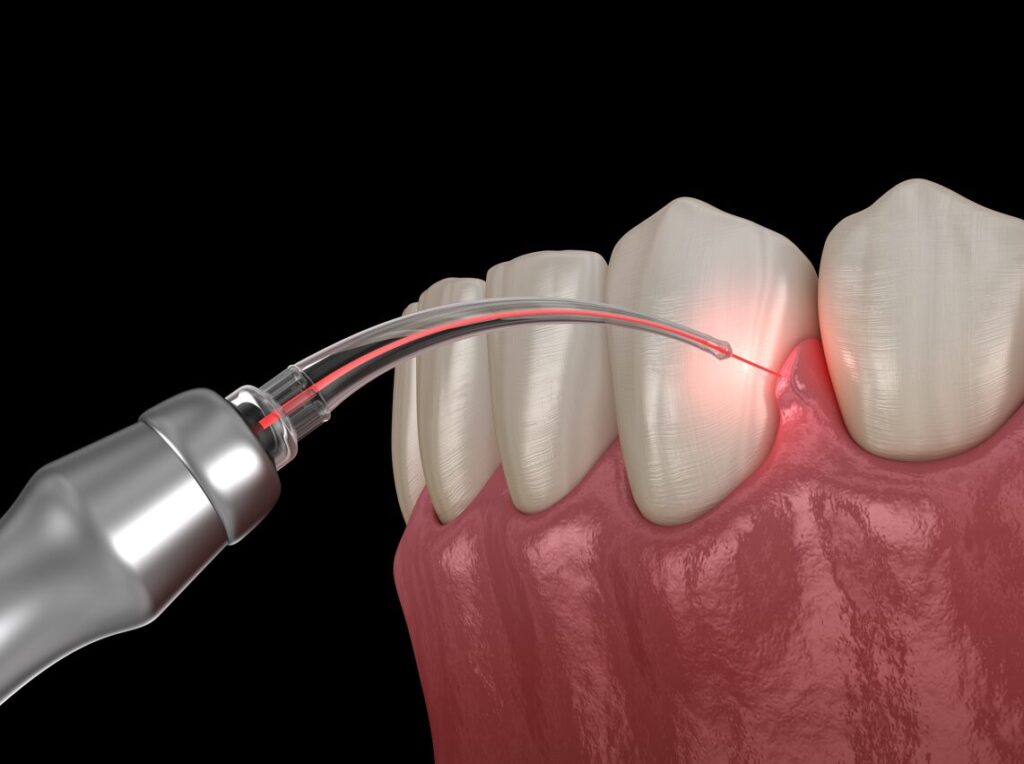
- Scaling and Root Planning: Thorough cleaning procedures that effectively eliminate plaque and tartar from beneath the gumline while also smoothing the root surfaces.
- Advanced cases may require surgical interventions such as flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration.
- Medical Treatment: In instances of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed, either systemically or locally.
4. Dental Trauma Management
- Urgent Assistance: Prompt attention to stabilize the tooth, alleviate discomfort, and avoid additional harm.
- Restorative Treatment: Various options are available to address the damage, such as dental bonding, crowns, or root canal therapy, depending on the severity.
- Stabilizing a loose or dislodged tooth using a splint.
5. Treating a Dental Abscess
- Drainage: Performing an incision and drainage procedure to eliminate the accumulation of pus and alleviate pressure.
- Prescription Medication: Systemic prescription medication to manage infection.
- Root Canal Therapy: Eliminating the source of infection if it affects the tooth pulp.
- Extraction: In more serious situations where the tooth cannot be saved,.
6. Addressing Discomfort from Tooth Eruption
- Pain Relief Options: Consider using topical analgesics such as teething gels for children or over-the-counter pain relief gels for adults.
- Pain Relief for Oral Discomfort: Utilize acetaminophen or ibuprofen to effectively manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Soathing saltwater rinses are a gentle way to alleviate gum discomfort.
7. Treating Bruxism
- Night Guards: Custom-fitted dental appliances designed to safeguard teeth against grinding and clenching while sleeping.
- Stress Management: Utilizing various techniques like relaxation exercises, counseling, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments to effectively address and alleviate the impact of stress on bruxism.
- Dental Corrections: Improving bite alignment through orthodontic treatment or restorative procedures.
8. Treating Toothache Associated with Sinusitis
- Medications for reducing nasal congestion and sinus pressure, available either over-the-counter or with a prescription, are called decongestants.
- Clearing nasal passages and reducing inflammation can be achieved through the use of saline solutions for nasal irrigation.
- Medication: In the case of bacterial sinus infections, a course of medication may be prescribed.
9. Dealing with Referred Pain
- Treatment options for TMJ disorders can include the use of oral appliances, physical therapy, medications, and, in more severe cases, surgery.
- Neuralgia can be effectively managed with medications like anticonvulsants or nerve blocks to alleviate pain.
Taking Preventive Measures
It is essential to prioritize prevention in order to minimize the chances of experiencing toothache. Here are some strategies to help prevent health issues:
1. Maintaining Good Oral Health

- Oral Hygiene: Maintain a regular oral hygiene routine by brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. This helps to effectively remove plaque and protect against cavities.
- Make sure to floss every day to effectively clean between your teeth and below the gumline.
- Mouthwash: Incorporate the use of an antimicrobial mouthwash to effectively combat plaque and bacteria.
2. Consistent Dental Appointments
- Regular dental check-ups: Routine examinations and cleanings to identify and tackle any issues at an early stage.
- Thorough Cleanings: Elimination of tartar and plaque buildup that is difficult to remove through regular brushing and flossing.
3. Adjusting Your Diet
- Cut Back on Sugary Foods and Drinks: It’s a good idea to reduce your intake of foods and beverages that are high in sugar in order to help prevent cavities.
- Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet: A well-rounded diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and calcium can greatly contribute to maintaining good dental health.
4. Taking precautions
- Be cautious with your diet. It’s important to avoid chewing on hard objects such as ice and hard candies, as they can potentially lead to tooth fractures.
- Protect Your Smile: Don’t forget to wear mouth guards while participating in sports and physical activities to keep your teeth safe from potential injuries.
5. Making adjustments to your daily routine
- Stress Management: Take steps to reduce stress and prevent bruxism and other dental issues.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking poses a considerable threat to periodontal health and can lead to various oral health problems.

Conclusion
Dealing with a toothache can be quite a challenge, but by gaining insight into what triggers it and considering suitable remedies, you can find ways to effectively manage and alleviate the pain. Timely intervention by dental professionals is crucial when it comes to addressing pain caused by various dental issues such as cavities, pulpitis, periodontal disease, and more. Maintaining oral health and preventing toothache requires implementing preventive measures such as practicing good oral hygiene, scheduling regular dental visits, and making lifestyle modifications. By taking a comprehensive approach to oral health, individuals can experience lasting benefits and better overall well-being.